What Is Car Credit?
Having car credit means you financed a car before and payments have been reported to the credit bureaus. No car credit means you never financed a vehicle before.
Click Here To Join Our Mailing List For Credit & Money Tips!
When considering the purchase of a new or used vehicle, one crucial aspect to understand is car credit. This term encompasses various elements related to financing a car purchase, including credit scores, loan types, and the impact of your credit history. In this article, we will explore what car credit is, how it works, and why it matters.
What is Car Credit?Car credit refers to the creditworthiness of an individual in the context of acquiring a vehicle. It involves the ability to secure financing for purchasing a car and the terms under which that financing is obtained. Essentially, it’s about how lenders assess your financial reliability to determine whether to extend a loan for a vehicle.
Car credit can impact various aspects of buying a vehicle, including the interest rate on the loan, the loan amount, and the length of the loan term. Understanding car credit is crucial for making informed financial decisions when buying a car.
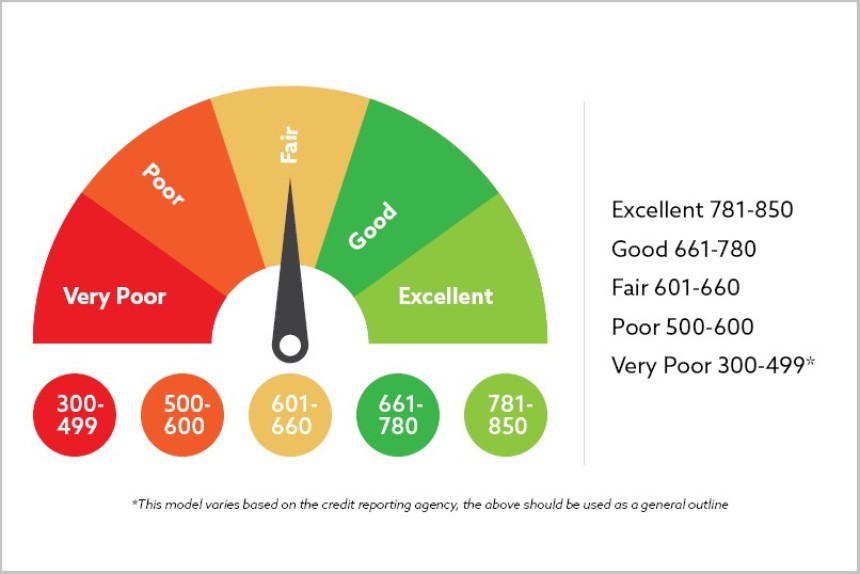
Key Components of Car Credit- Credit Score: Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. It typically ranges from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better credit health. Credit scores are influenced by factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and recent credit inquiries.
- Credit Report: Your credit report provides a detailed history of your credit accounts, including loans, credit cards, and payment history. It also includes any negative information such as late payments or bankruptcies. Lenders use your credit report to assess your financial responsibility.
- Loan Terms: The terms of a car loan include the interest rate, the loan amount, and the duration of the loan. A better credit score generally means more favorable loan terms, such as a lower interest rate or a larger loan amount.
- Down Payment: A down payment is the amount of money you pay upfront when purchasing a vehicle. A larger down payment can reduce the loan amount needed and may improve your chances of securing a loan with favorable terms.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): This ratio compares your total monthly debt payments to your monthly income. Lenders use this ratio to assess your ability to manage additional debt. A lower DTI indicates that you have a manageable level of debt relative to your income.
When you apply for a car loan, lenders will evaluate your car credit to determine your eligibility and the terms of the loan. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the process:
- Application: You begin by applying for a car loan through a bank, credit union, or dealership. The lender will request information about your income, employment status, and financial history.
- Credit Check: The lender will pull your credit report and score to assess your creditworthiness. They will review your credit history, including payment history, outstanding debts, and any negative marks.
- Loan Assessment: Based on your credit score and report, the lender will determine the loan amount you qualify for, the interest rate, and the loan term. Higher credit scores typically lead to better loan terms.
- Approval and Terms: If approved, you’ll receive a loan offer detailing the terms, including the interest rate, loan amount, and repayment schedule. You’ll need to review and accept the terms to finalize the loan.
- Purchase and Repayment: Once you accept the loan, you can proceed with purchasing the vehicle. You’ll then begin making regular payments according to the agreed-upon schedule.
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the terms of your car loan. Here’s how different credit score ranges generally affect car credit:
- Excellent Credit (750 and above): Individuals with excellent credit scores typically qualify for the lowest interest rates and the best loan terms. Lenders view them as highly reliable borrowers.
- Good Credit (700-749): Those with good credit scores also receive favorable loan terms, though the interest rates may be slightly higher than those offered to individuals with excellent credit.
- Fair Credit (650-699): Borrowers with fair credit may still secure a loan, but they might face higher interest rates and less favorable terms compared to those with higher credit scores.
- Poor Credit (below 650): Individuals with poor credit may struggle to obtain a loan or face significantly higher interest rates. They might also be required to make a larger down payment.
If your credit isn’t in the best shape, there are steps you can take to improve it before applying for a car loan:
- Check Your Credit Report: Obtain a copy of your credit report and review it for errors or discrepancies. Dispute any inaccuracies with the credit bureaus to ensure your report reflects your true credit history.
- Pay Bills on Time: Consistently paying your bills on time is crucial for maintaining a positive credit history. Late payments can significantly impact your credit score.
- Reduce Debt: Lowering your credit card balances and paying off outstanding debts can improve your credit utilization ratio, which can positively affect your credit score.
- Avoid New Credit Inquiries: Frequent credit inquiries can lower your credit score. Avoid applying for new credit accounts before applying for a car loan.
- Save for a Larger Down Payment: A larger down payment reduces the amount you need to borrow and can improve your chances of securing a loan with better terms.
If traditional car loans aren’t an option due to credit issues, consider alternative financing options:
- Buy Here, Pay Here Dealerships: These dealerships offer in-house financing and may be more lenient with credit requirements. However, they often come with higher interest rates.
- Credit Unions: Credit unions may offer more favorable terms and lower interest rates than traditional banks, especially if you’re a member.
- Co-Signers: Having a co-signer with better credit can improve your chances of securing a loan with better terms. However, the co-signer is responsible for the loan if you default.
- Leasing: Leasing a vehicle might be an option if you have less-than-perfect credit. Lease terms may be more flexible, though there may be mileage limits and other restrictions.
Understanding car credit is essential not only for securing a loan but also for managing vehicle ownership responsibly. Car credit affects not just the loan approval process, but also ongoing costs associated with car ownership, such as monthly payments and insurance premiums.
Maintaining good car credit can lead to lower interest rates and better financing options in the future, whether you’re buying another vehicle or seeking other types of loans. Additionally, good car credit reflects positively on your overall financial health, which can benefit you in various aspects of life.
Be SmartCar credit is a vital component of the vehicle purchasing process, encompassing your creditworthiness, the loan terms you receive, and how lenders assess your ability to repay a loan. By understanding the factors that influence car credit and taking steps to improve it, you can make informed decisions and secure favorable financing for your next vehicle purchase.
Whether you’re a first-time car buyer or looking to upgrade your current vehicle, being knowledgeable about car credit can help you navigate the financing process with confidence and ensure that you achieve the best possible terms for your car loan.